Legislative developments in relation to electronic invoicing have not ceased throughout 2021. More and more countries are seeing the need to legislate on e-invoicing and impose obligations.
2021 promised to be a year full of changes at a global level in terms of electronic invoicing regulation. And, although this has been the case, we have also seen delays due to the crisis caused by Covid-19.
The widespread adoption of e-invoicing will continue in 2022, driven by governments around the world. Read on to find out the most relevant developments for next year.
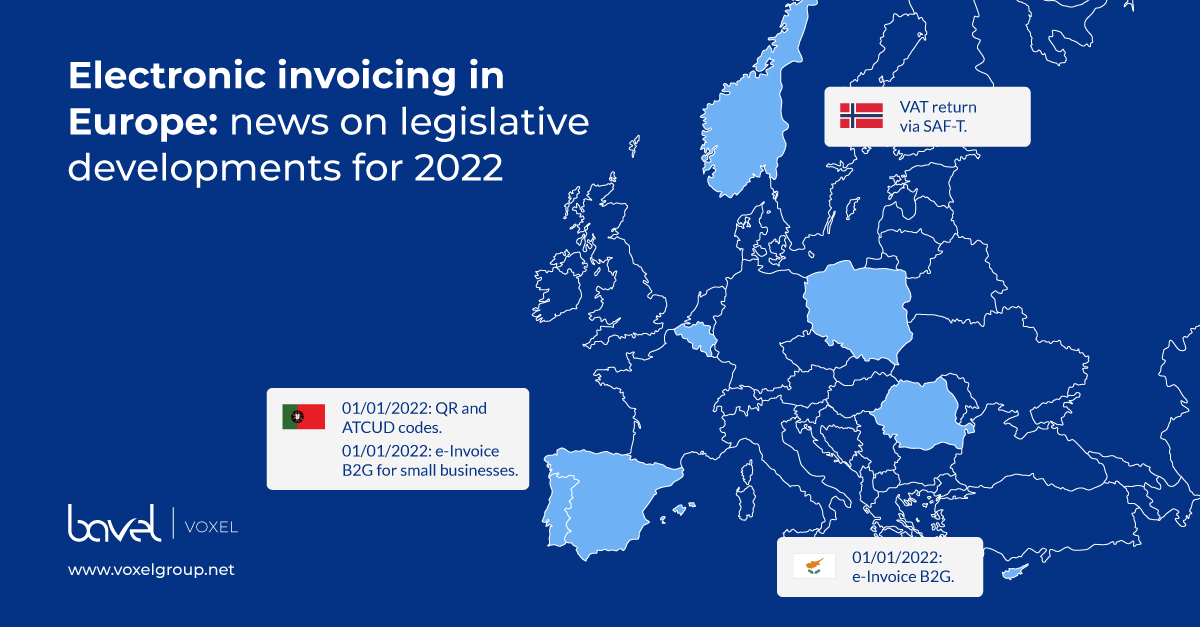
Portugal: QR codes and ATCUD are arriving
Portugal has been working for years on the implementation of electronic invoicing. After several changes, QR codes and ATCUD will finally come into force in 2022. From 1 January 2022, all invoices will have to include a unique identification number (ATCUD) and a QR code that includes all the information on the invoice.
Although this obligation should have been implemented in 2021, the Portuguese government considered that companies should invest their efforts in overcoming the crisis. However, a voluntary period was established for those companies that were already prepared.
1 January 2022 is also the deadline for small businesses to adopt mandatory electronic invoicing in the B2G environment. Large and medium-sized companies have done so throughout 2021.
Cyprus: B2G e-invoicing mandatory
Since April 2020, all Cypriot public administrations have been able to receive and process electronic invoices, in accordance with European Directive 2014/55/EU. However, it will not be until 1 January 2022 that B2G electronic invoicing becomes mandatory. This means that all public administration suppliers will have to use e-invoicing for their transactions with the government.
As in many other countries around the world, this step usually precedes the implementation of mandatory B2B e-invoicing.
Norway: SAF-T reporting system strengthened
Norwegian companies must prepare a mandatory report to the Norwegian Tax Agency using the SAF-T (Standard Audit File for Tax) standard from 2020. The Norwegian government is now going one step further and will oblige companies to report VAT digitally under the same system.
Other European countries
2022 will also be a key year for other European countries.
This is the case of Spain, for example, which plans to pass the Crea y Crece Law next year. The draft bill introduces the mandatory use of B2B e-invoicing. However, its use is not expected to be mandatory until at least 2023.
Belgium has confirmed its intention to introduce mandatory B2B e-invoicing in the country. The Ministry of Finance plans to publish a draft law with details on regulation, timing and practical implementation in 2022. Currently, B2B e-invoicing is allowed in Belgium, provided that both sender and receiver agree.
In January 2022 the Polish government will publish the Act regulating the rules of operation of the National e-Invoicing System. Although a voluntary period started at the end of 2021, it will not be until 2023 that B2B electronic invoicing will become mandatory in the country.
Finally, Romanian companies will have to start using the SAF-T (Standard Audit File for Tax) standard for their reporting from the first month of 2022.
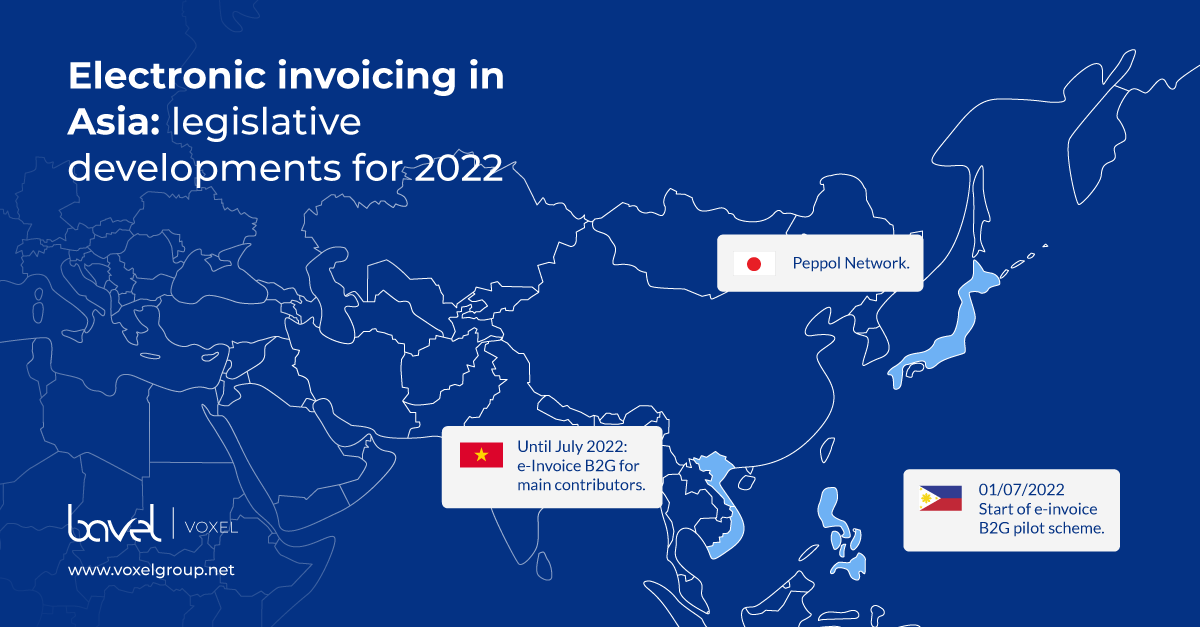
Japan joins the PEPPOL network
Peppol, which was initially created as a system to facilitate e-commerce in Europe, continues to cross borders. Japan’s Digital Agency has become the newest Peppol authority. Japan thus joins the network to facilitate the exchange of electronic transactions between companies in Japan and those in the rest of the Peppol network (31 European countries, Australia, Canada, Mexico, New Zealand, Singapore and the USA).
Pilot scheme for B2G e-invoicing starts in the Philippines
As other countries have already done, the Philippines will take the first step towards the implementation of e-invoicing in the country with a pilot scheme. In April, 6 companies will participate in the first tests. On 1 July 2022, the country’s main taxpayers will start transmitting their invoices to the government. This pilot scheme will serve to lay the groundwork for the country’s e-invoicing system.
The Philippines aims to make the use of e-invoicing widespread by 2023.
Mandatory B2B electronic invoicing is coming in Vietnam
In 2021, Vietnam started the roll-out of B2B invoicing in the country. Companies in 6 provinces (Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City, Hai Phong, Quang Ninh, Phu Tho and Binh Dinh) started the implementation of e-invoicing in their B2B transactions. The deadline for this first phase is March 2022.
Companies in the remaining 57 provinces will have to do the same from April until July 2022, in phase 2 of the project.
Vietnamese companies will have to transmit all invoices to the country’s tax authority and then to the tax issuer. In other words, they have adopted a clearance model for electronic invoices.
Panama completes its process
After the success of its pilot plan and the massification phase, electronic invoicing will be mandatory in Panama in 2022. As of 1 January 2022, it will be mandatory for taxpayers registered with RUC. And as of July 2022, it will be mandatory for all other companies.
United States moves towards e-invoicing
After working on the electronic invoice project, the pilot programme for the exchange of electronic invoices in the United States is expected to be operational in the course of next year.
If you don’t want to miss any news about electronic invoicing regulation in the world, subscribe to our monthly newsletter.